November 14, 2023
Japan Inflation: The Current State of the Japanese Economy
Understanding Japans Inflation Crisis and Its Impact on the Economy: Causes, Effects, and Potential Solutions
Learn about Japans inflation crisis and its impact on the economy in this article. Explore the causes, effects, and potential solutions to Japans prolonged low inflation, also known as Japans lost decades. Discover how the deflationary mindset in Japanese society has resulted in decreased consumer spending and stagnant economic growth.
Japan is a country known for its technological advancements, rich culture, and unique traditions. However, behind the scenes, the Japanese economy has been grappling with a persistent issue: inflation. In this article, we will delve into the topic of Japans inflation and explore its causes, effects, and possible solutions.
The Causes of Japans Inflation
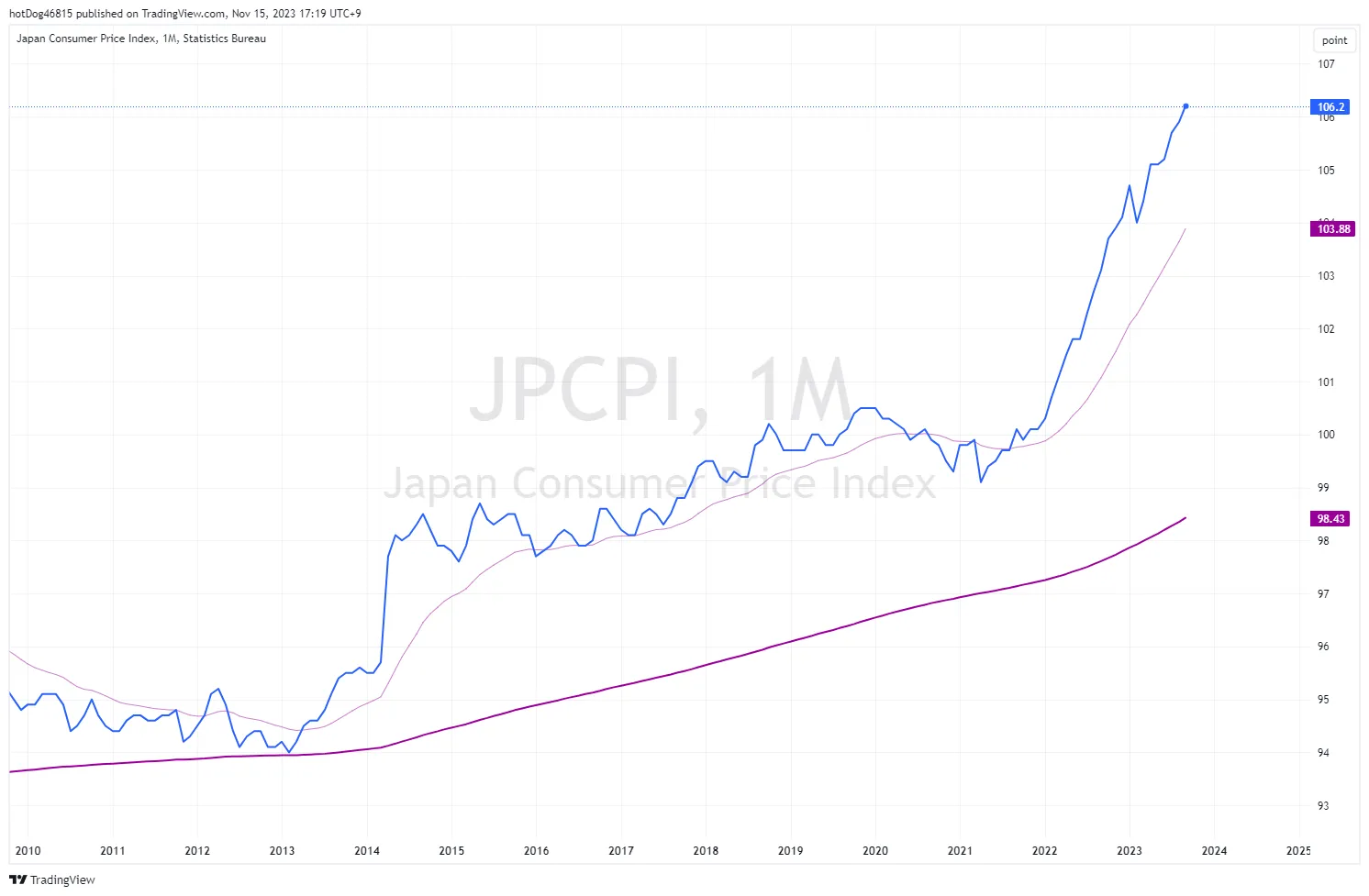
Japan has been experiencing a prolonged period of low inflation, often referred to as Japans lost decades. One of the primary causes of this issue is the deflationary mindset that has taken hold in Japanese society. Consumers have become accustomed to waiting for prices to drop further before making purchases, leading to decreased consumer spending and stagnant economic growth.
Another contributing factor to Japans inflation woes is the countrys rapidly aging population. As the population ages, there is a decline in the workforce, which leads to a decrease in consumption and overall economic activity. This demographic shift places additional pressure on the economy, making it challenging to stimulate inflation.
The Effects of Japans Inflation
The persistent low inflation in Japan has had several detrimental effects on the economy. Firstly, it hinders the Bank of Japans efforts to reach its inflation target of 2%. Despite implementing various monetary stimulus measures, such as quantitative easing and negative interest rates, the desired level of inflation remains elusive.
Furthermore, low inflation has implications for Japans overall economic growth. When prices remain stagnant or decline, businesses find it challenging to increase profits and invest in expansion. This lack of investment slows down economic growth, making it difficult for Japan to overcome its deflationary environment.
Closer Look at People's Life
Taking bigmac for example, it increased its price around 30% since 2022.
| JPY | USD | |
| Before March 2022 | 390 | 2.60 |
| March 2022 | 390 | 2.60 |
| September 2022 | 410 | 2.73 |
| January 2023 | 450 | |
| July 2023 | 500 |
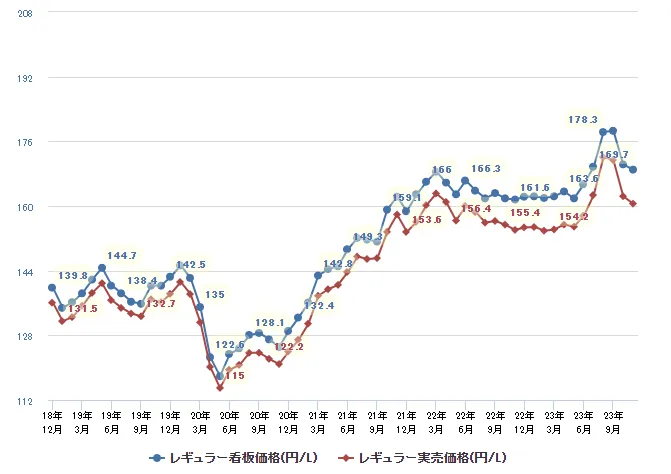
Gas price also increased. From March 2020 to now, 50% increase. However, the government subsidises gas suppliers since 2022 to pushing down the price hike.
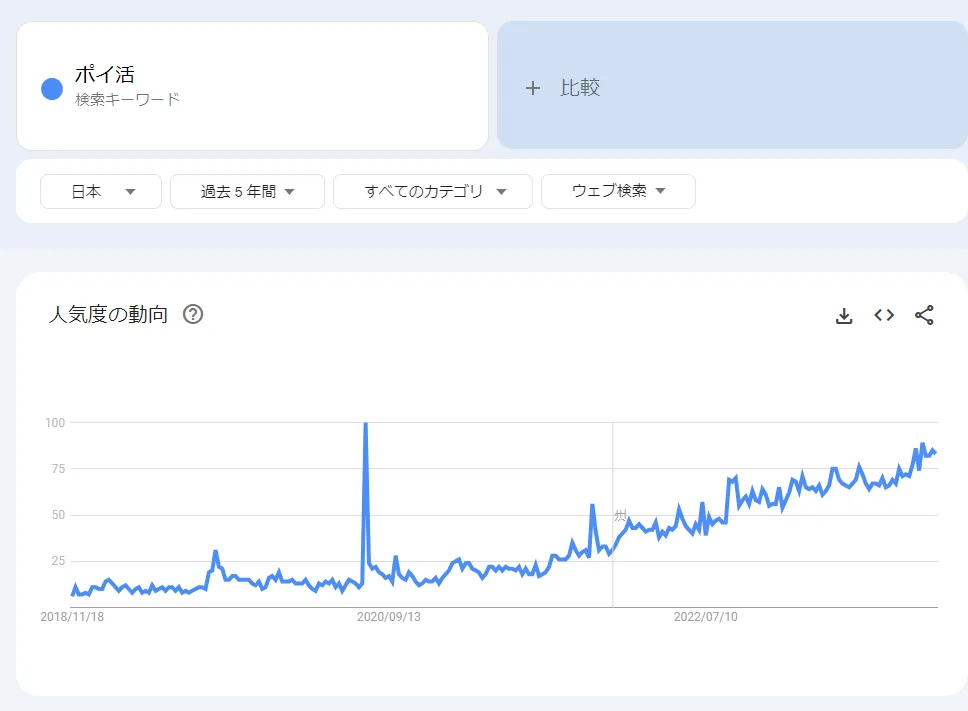
To tackle with those high price issues, people started to do Poi-Katsu (Point Katsudou), micro reward programs by different types of service providers. It's growing trend since 2018.
Here's the major reward program points.
- T Point by CCC
- Ponta Point by by LM (owned by Mitsubishi)
- Rakuten Point by Rakuten
- nanaco Point by Seven & I holdings
- d Point by NTT docomo
- WAON Point yb AEON corporation
- LINE Point by LY corporation
Possible Solutions for Japans Inflation
Japan faces a complex challenge in trying to combat low inflation. Implementing a combination of monetary and fiscal policies has been the approach taken by the Japanese government and the Bank of Japan.
The government has initiated fiscal stimulus measures to boost consumer spending and encourage investment. These policies aim to improve economic sentiment and break the deflationary cycle. Additionally, the Bank of Japan continues to explore unconventional monetary policies to stimulate inflation and promote economic growth.
Conclusion
Japans struggle with low inflation presents a significant obstacle to its economy. The causes of this ongoing issue are multifaceted, including a deflationary mindset and an aging population. However, with the governments fiscal measures and the Bank of Japans monetary policies, there is hope for a turnaround. Ultimately, achieving a healthy level of inflation is crucial for the Japanese economy to thrive.